Category: TFS
Using Git with Visual Studio 2013
In this post I’ll outline how to make code changes when using Git with Visual Studio. This applies regardless of where git is hosted (TFS, GitHub or elsewhere).
Git differs from other source control because of its “branch often” philosophy. Plus the fact that you have a copy of the entire repository on your local machine! But despite the fact that TFS tries to make the process easy, there’s still a process to follow when doing development. Best practice dictates that instead of just checking our changes into origin/master (the “upstream repository”), we’ll want to do the following:
- Create a local branch
- Do your work and commit changes
- Merge changes with local master
- Push changes to upstream master
Note that in some cases, origin/master will NOT be our upstream repository. For example, we might be working off a Development branch. So make adjustments as appropriate when following this guide.
I’m going to assume that you’re already set up with your repository, either through TFS or by using the method outlined in my blog. Let’s say you’re ready to develop.
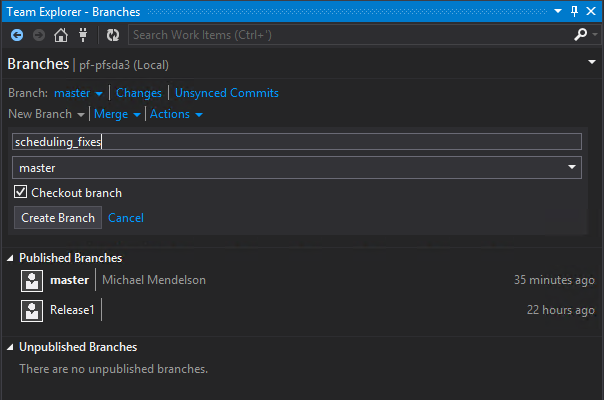
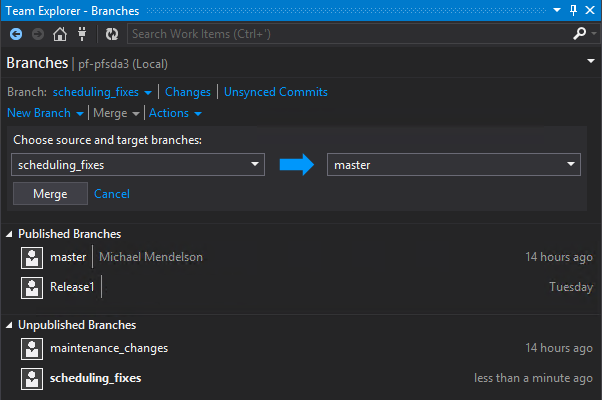
Create a branch
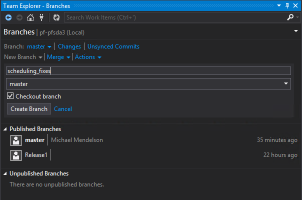
- At the TFS main menu, click on Branches
- Click on New Branch and set the name.
- Click on Create Branch.
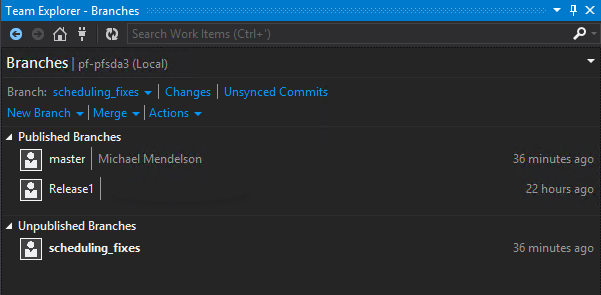
You’ll see your new branch under “Unpublished Branches”. In TFS, “unpublished” means that the branch exists only locally. Note that the value of the branch dropdown has been changed. You are now working on the new branch that you’ve created.
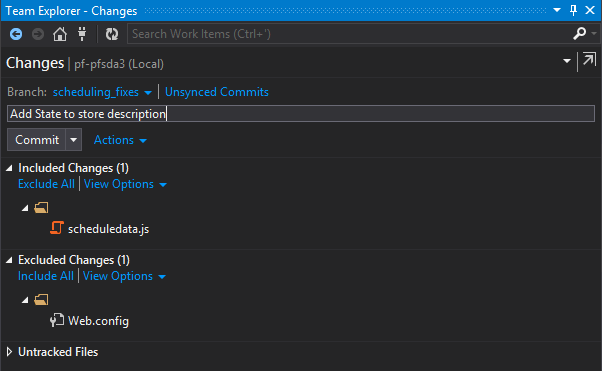
Do your work and commit changes
- Go to the Changes view. Your changed items will be listed.
- Add a comment for your commit (required).
- Click Commit. Changes are committed locally.
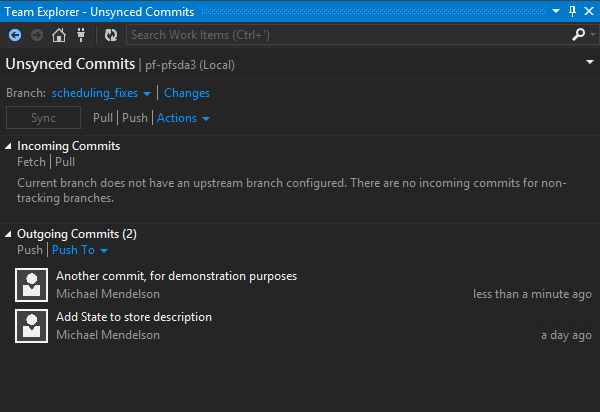
Merge your changes
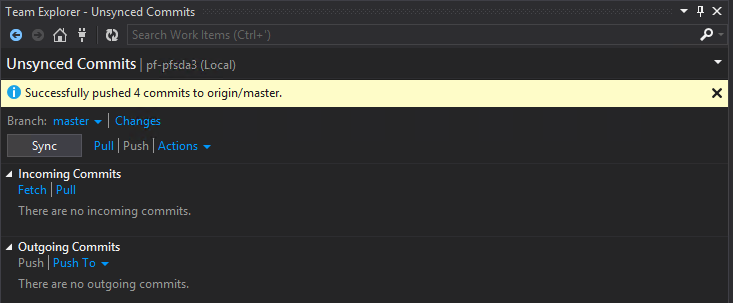
Once you’re done and are ready to contribute your changes to the upstream server, your Unsynced Commits tab might look something like this:
- In the Merge tab, click on the Merge dropdown.
- Set it up to merge the changes to your local master.
- Click Merge.
Since this is your LOCAL master, you’re unlikely to have conflicts. Notice that you’ve been automatically switched to the master branch. You’re done with your old branch, and it can be deleted if appropriate.
Push your changes
Time to push your changes upstream! From the Unsynced commits tab, do the following:
- Click Pull to merge all changes locally.
- Address any conflicts between our check-ins and the merged ones.
- Retest the code as necessary.
- Push again.
Note: The Sync button will both pull and push in a single step. The problem with this approach is that you don’t have the opportunity to test any merged changes!
If your local repository is in sync with the upstream server, you can simply push without the pull. But to avoid an error, simply pull first.
If your push was successful, you’ll get the following:
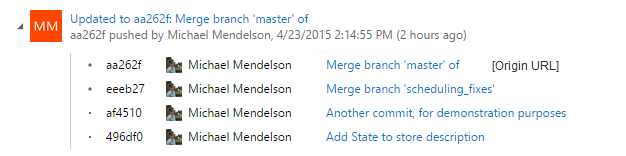
Success! When I view the history in TFS, my merge looks like this:
Related: Getting started with Git/TFS (relates to git hosted on TFS)
Getting started with Git/TFS
I recently moved one of my projects to a TFS Git repository. But Git did not start out as a Microsoft product, and Git is a relatively recent addition to TFS. The TFS Visual Studio tools give us some powerful shortcuts, but some things can only be done on the command line. Here’s how to get the best of both worlds.
Related: Using Git with Team Foundation Server and Visual Studio 2013
Install Git
If you haven’t done so, you’ll need to install Git. This will allow you to run the command line tools, and (as an added bonus) you’ll get a BASH shell as well. So if you ever wanted to have a Linux shell on your Windows box, now’s your chance. IMO it’s good to know Linux, but hey, I’m not here to lecture.
- Go to http://git-scm.com/download/win
- There are three options in the install. They can be a bit involved, but they’re worth reading carefully. If you’re avoiding the BASH shell, you’ll want to choose the option to make git available in the Widows path.
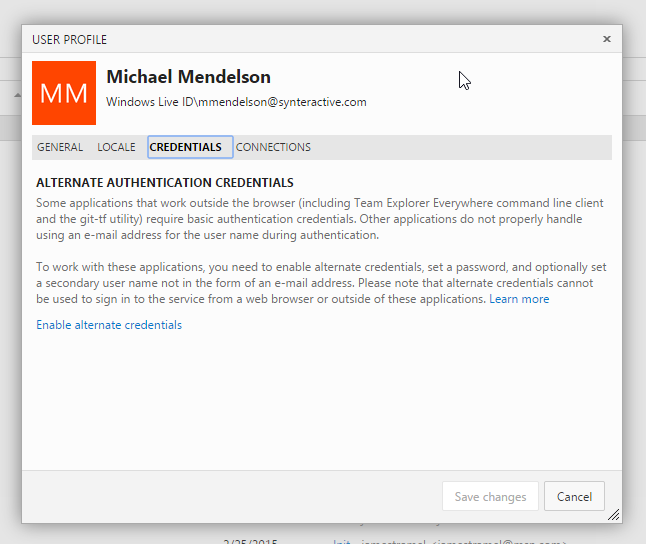
Set up alternate credentials in TFS
The first thing I found was that my Microsoft Online user name and password don’t work, when attempting to authenticate against git. A bit of research revealed that I had to take an additional step.
- Navigate to the git url for your git repository, and log in. In my case it was something like http://companyname.visualstudio.com/DefaultCollection/_git/rep-name/
- Click on your user name -> My profile -> Credentials. Click on the link at the bottom “Enable alternate credentials”, and create an alternate credential.
Clone your project
With Git, the way to get started with a project is to clone it. Among other things, this copies the entire repository to your working directory.
- Go back to the command line and issue the clone command:
git clone http://companyname.visualstudio.com/DefaultCollection/_git/rep-name/
- When prompted, use the alternate user name and password that you just set up.
The clone command will replicate the project on your local machine, and you’re good to go.
Most commands (including clone) can be performed directly in Dev Studio, but the command line will be there if you need it.